Understanding Men’s Balding and Male Pattern Baldness

Hair loss is a common concern among men, and it can affect one's self-esteem and confidence. One of the most prevalent causes of patchy hair loss in men is male pattern baldness; also known as androgenetic alopecia. Genetics and other factors play a crucial role in determining a man's risk of developing male pattern hair loss.
There are several types of hair loss that men may experience:
- Androgenetic Alopecia: Male pattern baldness — called androgenetic alopecia (or androgenic alopecia) — is the most common cause of hair loss in men. It is genetic and characterized by a receding hairline and thinning or baldness on the crown of the head. This condition occurs because the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) shrinks hair follicles, making them unable to produce new hair.
- Alopecia Areata: This type of thinning hair appears as small bald patches on the scalp or other parts of the body. It is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, iron deficiency anemia, and fungal infections can contribute to male hair loss. Treating the underlying medical issue may help in restoring hair growth.
Male pattern hair loss primarily has genetic roots. Family history plays a significant role. If your father or grandfather had hair loss, you are more likely to develop it because of shared genetic factors.
The androgen receptor gene (AR) plays a major role in male pattern baldness. According to several studies, variations in this gene can make some individuals more susceptible to hair loss. When this gene is sensitive to androgens, it can trigger the hair follicles to shrink and eventually stop producing new hair.
Androgens are a helpful tool for your body's development. Among other things, they help control the cycle of hair growth. If the androgens are overstimulated, your hair may start thinning.
Androgenic variations in several genes affect how your hair follicles will respond to Dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Over time, DHT shrinks hair follicles, causing them to produce finer and shorter hair until they eventually stop producing hair altogether.
Scientists identified a link between male pattern hair loss and several genetic variants. These variants, found in different regions of the genome, can increase the risk of baldness. This research shows the intricate genetics of male baldness and can help doctors determine if men carry the variant for hair loss earlier.
Traditionally, male pattern baldness manifests in thinning hair at the temples. This thinning progresses backwards up the scalp in an "M" shape. This is commonly seen as a noticeably receding hairline.
After first affecting the hairline, male pattern baldness usually progresses to a bald spot on the crown of the head. If left untreated, the thinning at the temples and bald spots will eventually meet and merge. There will usually be a horse-shoe shape of hair left over extending from the ears around the back of the scalp.
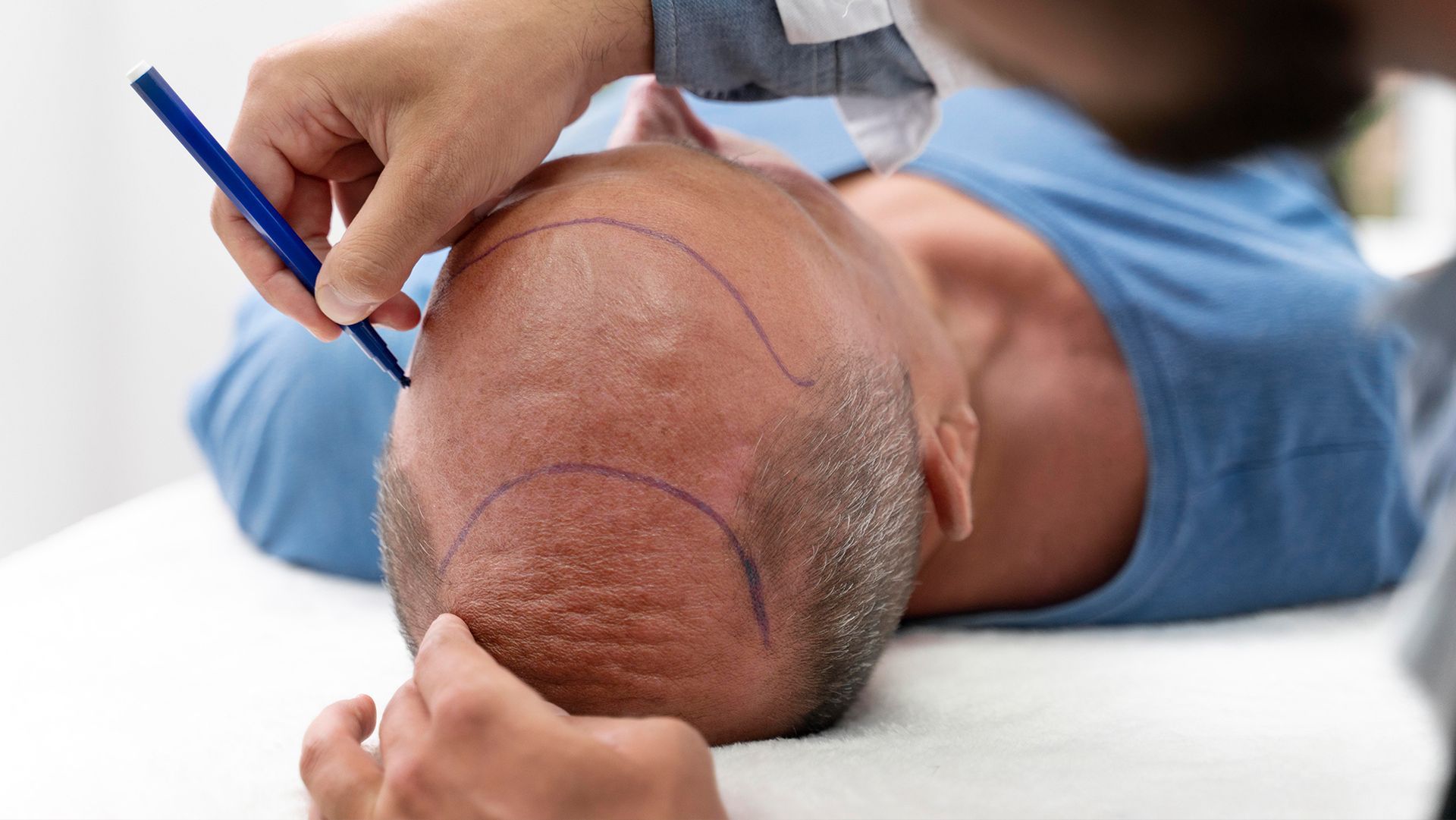
We need more research to effectively diagnose male pattern baldness. Thankfully, there are plenty of treatment options and hair restoration solutions to slow the rate of hair thinning in men:
- Medical treatments: Several medical treatments are available to combat male pattern hair loss, including:
- Minoxidil: A topical solution that stimulates hair growth and can slow down hair loss.
- Finasteride: An oral medication that reduces DHT levels, helping to prevent further hair loss and promote hair regrowth.
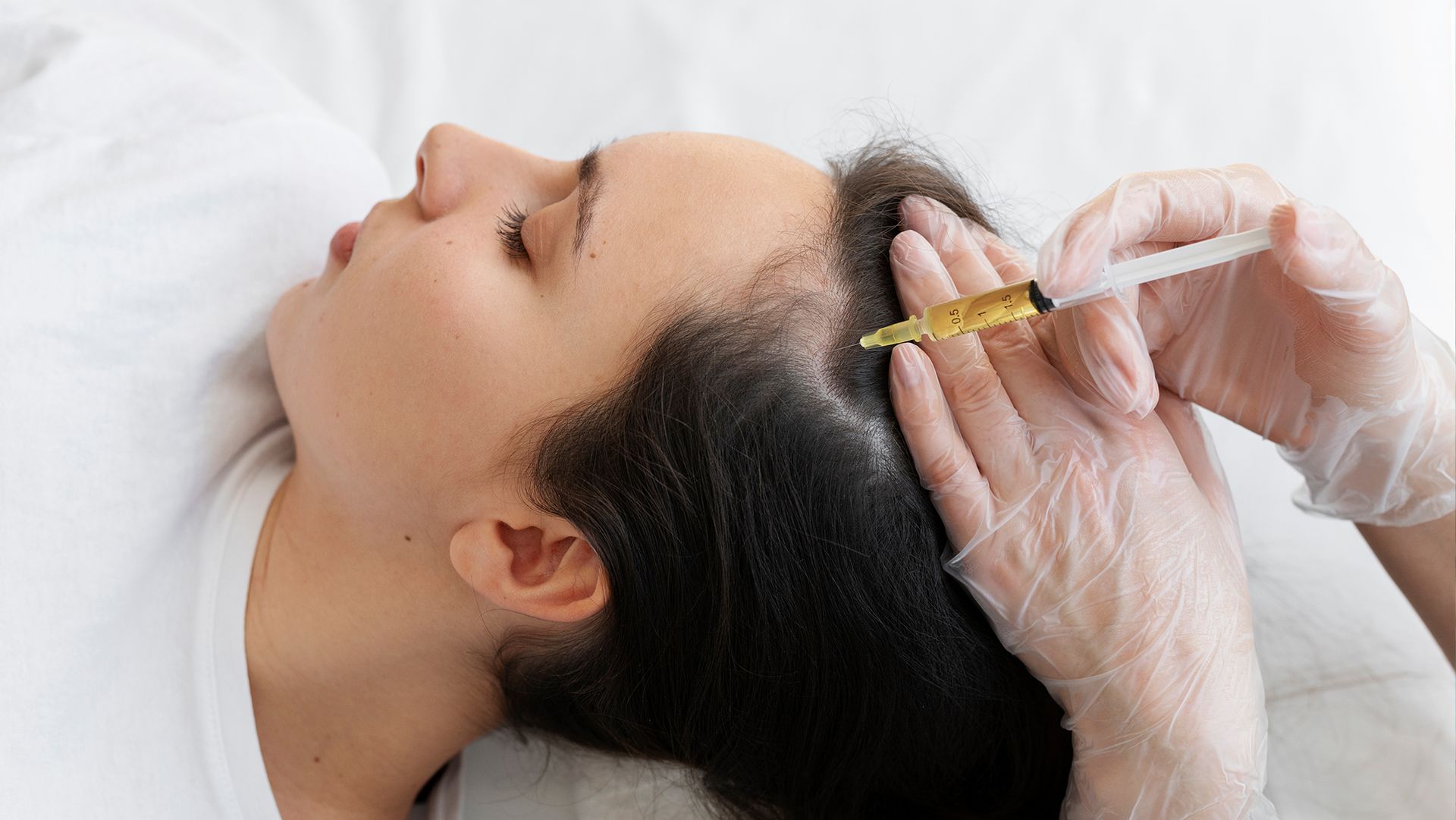
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) Therapy: Involves injecting your blood's plasma into your scalp to stimulate hair growth.
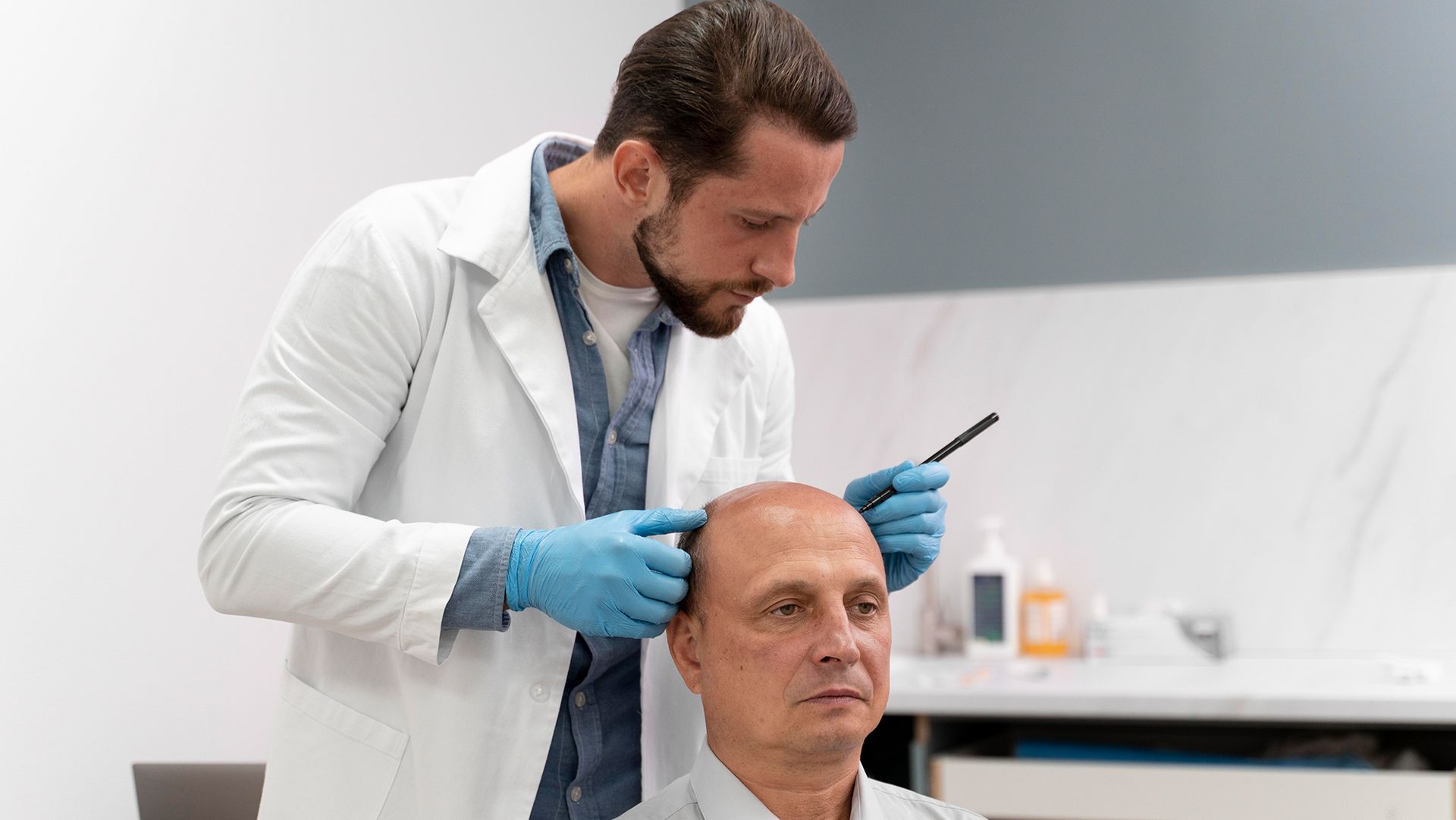
- Hair Transplant Surgery: Surgeons transplant healthy hair follicles into balding areas of the scalp.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and stress management, can help reduce hair loss.
- Preventive measures: Early intervention is essential to prevent male pattern baldness from worsening. Recognizing the signs and seeking treatment can slow down or even reverse the process.
Male pattern baldness is a lifelong condition, but it is manageable with the right treatment and care. The earlier you address the issue, the better the chances of preserving your hair. Beyond the physical effects, like a receding hairline and bald spots, permanent hair loss can also have emotional and psychological consequences. It can lead to reduced self-esteem and body image concerns, affecting a man's overall well-being and confidence.
Men and women can both suffer from androgenetic alopecia, although it is far more prevalent in men. Female pattern hair loss manifests a bit differently, with hair thinning towards the crown of the head. To learn more about hair restoration options for women, check out this article.
Going bald can be a distressing experience, but it is essential to remember that you are not alone. By learning about the causes and treatment options available, you can take proactive steps to manage hair loss.
There is plenty more information about hair restoration treatments and their side effects for you to explore here. Contact Dr. Yates to help create a personalized treatment plan to regain your confidence and maintain a healthy head of hair!